 网络模块封装
网络模块封装
# 一、主要内容
- 常见的网络请求模块,以及优缺点对比。
- JSONP的原理和封装
- JSONP原理回顾
- JSONP请求封装
- axios的内容详解
- 认识axios网络模块
- 发送基本请求
- axios创建实例
- axios拦截器的使用
# 二、 模块的选择
选择什么网络模块?
- Vue中发送网络请求有非常多的方式, 那么, 在开发中, 如何选择呢?
- 选择一: 传统的Ajax是基于XMLHttpRequest(XHR)
- 为什么不用它呢?
- 非常好解释, 配置和调用方式等非常混乱.
- 编码起来看起来就非常蛋疼.
- 所以真实开发中很少直接使用, 而是使用jQuery-Ajax
- 为什么不用它呢?
- 选择二: 在前面的学习中, 我们经常会使用jQuery-Ajax
- 相对于传统的Ajax非常好用.
- 为什么不选择它呢?
- 完全没有必要为了用网络请求就引用这个重量级的框架
- Vue的代码才1w+行.
- jQuery的代码1w+行.
- 那么, 就意味着为了方便我们进行一个网络请求, 特意引用一个jQuery, 你觉得合理吗?
- 首先, 我们先明确一点: 在Vue的整个开发中都是不需要使用jQuery了.
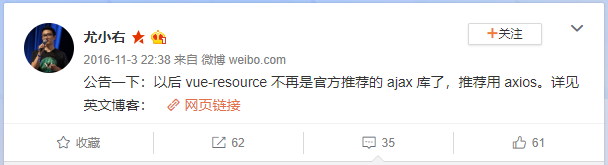
- 选择三: 官方在Vue1.x的时候, 推出了Vue-resource.
- Vue-resource的体积相对于jQuery小很多.
- 另外Vue-resource是官方推出的.
- 为什么不选择它呢?
- 在Vue2.0退出后, Vue作者就在GitHub的Issues中说明了去掉vue-resource, 并且以后也不会再更新.
- 那么意味着以后vue-reource不再支持新的版本时, 也不会再继续更新和维护.
- 对以后的项目开发和维护都存在很大的隐患.
- 选择四: 在说明不再继续更新和维护vue-resource的同时, 作者还推荐了一个框架: axios为什么不用它呢?
- axios有非常多的优点, 并且用起来也非常方便.
- 稍后, 我们对他详细学习.
# 三、 jsonp封装
# 1、jsonp
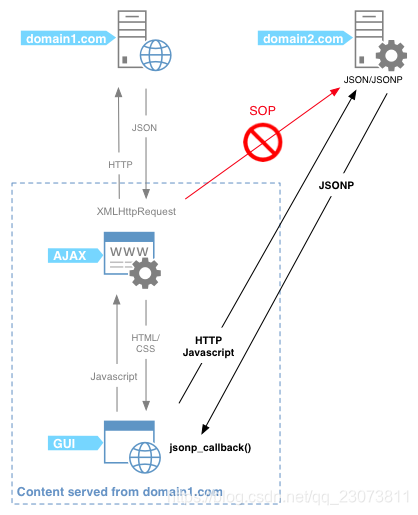
- 在前端开发中, 我们一种常见的网络请求方式就是JSONP
- 使用JSONP最主要的原因往往是为了解决跨域访问的问题.
- JSONP的原理是什么呢?
- JSONP的核心在于通过**<script>标签的src**来帮助我们请求数据.
- 原因是我们的项目部署在domain1.com服务器上时, 是不能直接访问domain2.com服务器上的资料的.
- 这个时候, 我们利用<script>标签的src帮助我们去服务器请求到数据, 将数据当做一个javascript的函数来执行, 并且执行的过程中传入我们需要的json.
- 所以, 封装jsonp的核心就在于我们监听window上的jsonp进行回调时的名称.
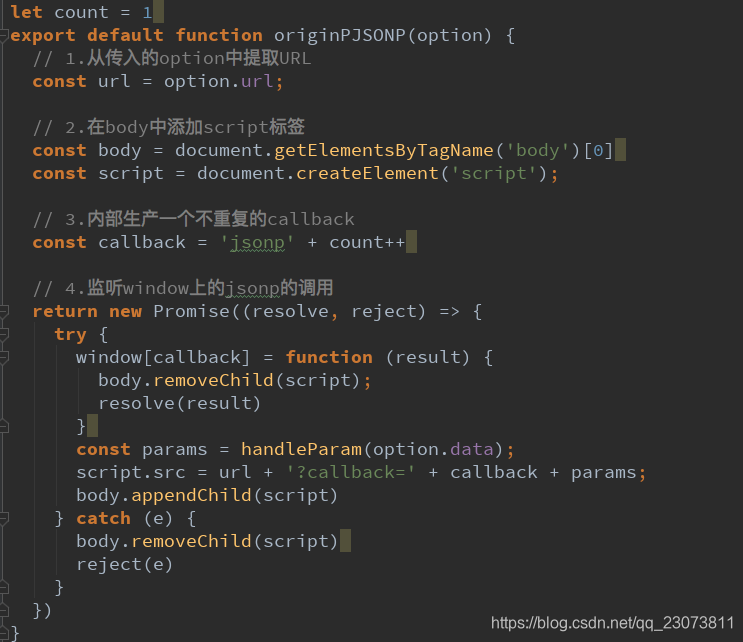
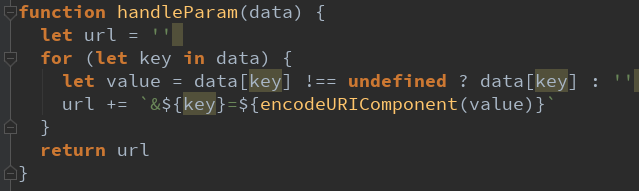
- JSONP如何封装呢?
- 我们一起自己来封装一个处理JSONP的代码吧.
# 2、JSONP封装
# 四、 认识 axios
# 1、为什么选择axios?
- 为什么选择axios? 作者推荐和功能特点
功能特点:
- 在浏览器中发送 XMLHttpRequests 请求
- 在 node.js 中发送 http请求
- 支持 Promise API
- 拦截请求和响应
- 转换请求和响应数据
- 等等
补充: axios名称的由来? 个人理解
- axios: ajax i/o system.
- 没有具体的翻译.
axios=ajax+promise
# 2、axios请求方式
- 支持多种请求方式:
- axios(config)
- axios.request(config)
- axios.get(url[, config])
- axios.delete(url[, config])
- axios.head(url[, config])
- axios.post(url[, data[, config]])
- axios.put(url[, data[, config]])
- axios.patch(url[, data[, config]])
- 如何发送请求呢?
- 我们看一下下边的案例
# 五、axios 发送基本请求
// 安装axios
npm install axios --save
1
2
2
# 1、发送 get 请求演示

- main.js代码
import axios from 'axios'
// 1.axios的基本使用 axios(config)
axios({
url: 'http://123.207.32.32:8000/home/multidata', // 项目接口
// !!! 默认是get请求 可以用method指定
// method: 'post'
}).then(res => { // 获取返回的数据
console.log(res);
})
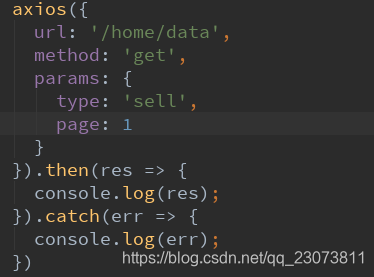
axios({
// url:'http://123.207.32.32:8000/home/data?type=sell&page=1'
// 参数除了可以直接拼接在url,也可以用params
url: 'http://123.207.32.32:8000/home/data',
// 专门针对get请求的参数拼接
params: {
type: 'pop',
page: 1
}
}).then(res => {
console.log(res);
})
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
# 2、发送并发请求
- 有时候, 我们可能需求同时发送两个请求
- 使用axios.all, 可以放入多个请求的数组.
- axios.all([]) 返回的结果是一个数组,使用 axios.spread 可将数组 [res1,res2] 展开为 res1, res2
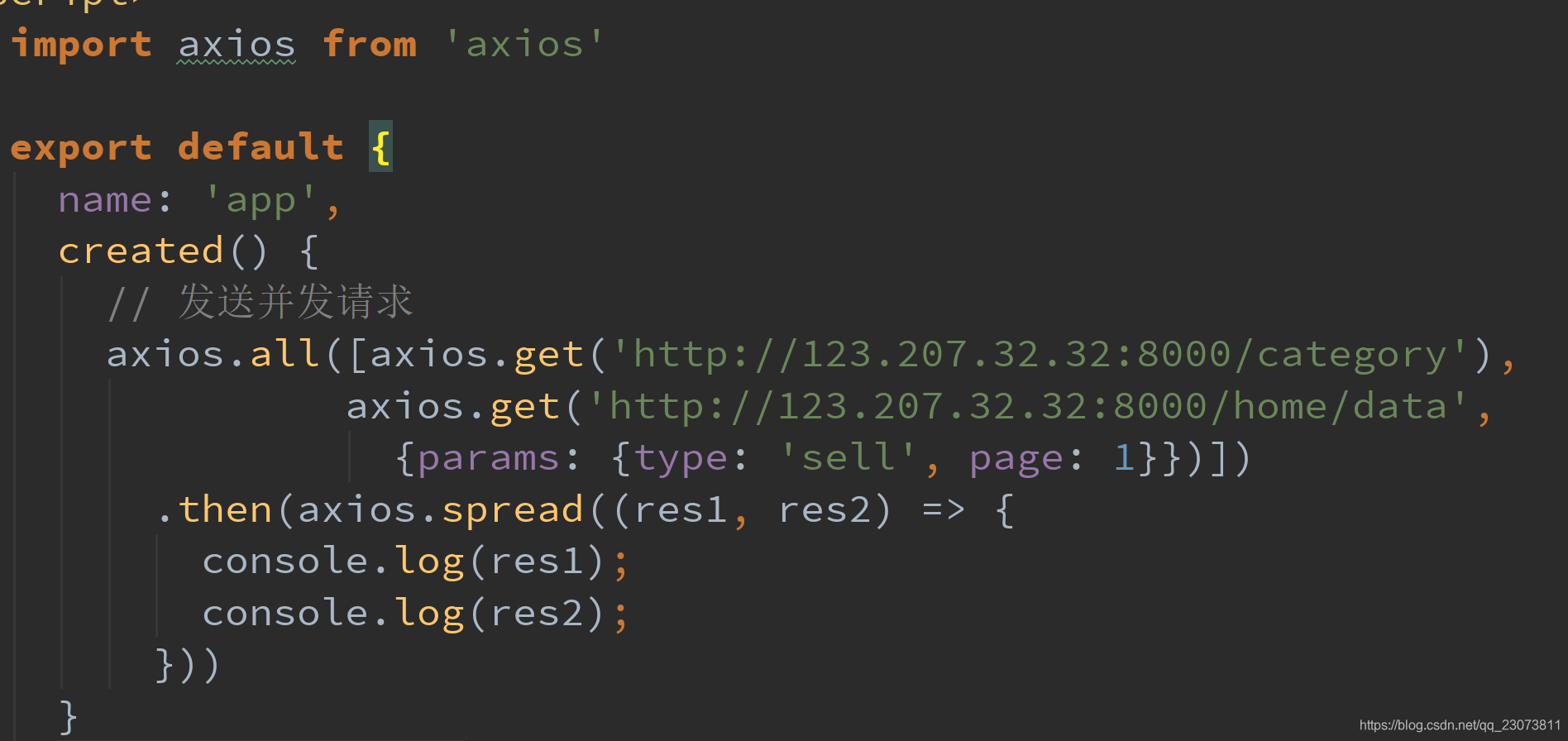
- 代码
// 2.axios发送并发请求(同时发多个请求,同时到达之后才能往下写代码)
// axios.all([axios(),axios()]).then(reslut=>{})
axios.all([axios({
url: 'http://123.207.32.32:8000/home/multidata'
}), axios({
url: 'http://123.207.32.32:8000/home/data',
params: {
type: 'sell',
page: 5
}
})]).then(results => {
console.log(results);
console.log(results[0]);
console.log(results[1]);
})
// .then()也可以写成
axios.all([axios({
url: 'http://123.207.32.32:8000/home/multidata'
}), axios({
url: 'http://123.207.32.32:8000/home/data',
params: {
type: 'sell',
page: 5
}
})]).then(axios.spread((res1, res2) => {
console.log(res1);
console.log(res2);
}))
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
# 3、全局配置
- 在上面的示例中, 我们的BaseURL是固定的
- 事实上, 在开发中可能很多参数都是固定的.
- 这个时候我们可以进行一些抽取, 也可以利用axiox的全局配置
axios.defaults.baseURL = ‘123.207.32.32:8000’
axios.defaults.headers.post[‘Content-Type’] = ‘application/x-www-form-urlencoded’;
1
2
2
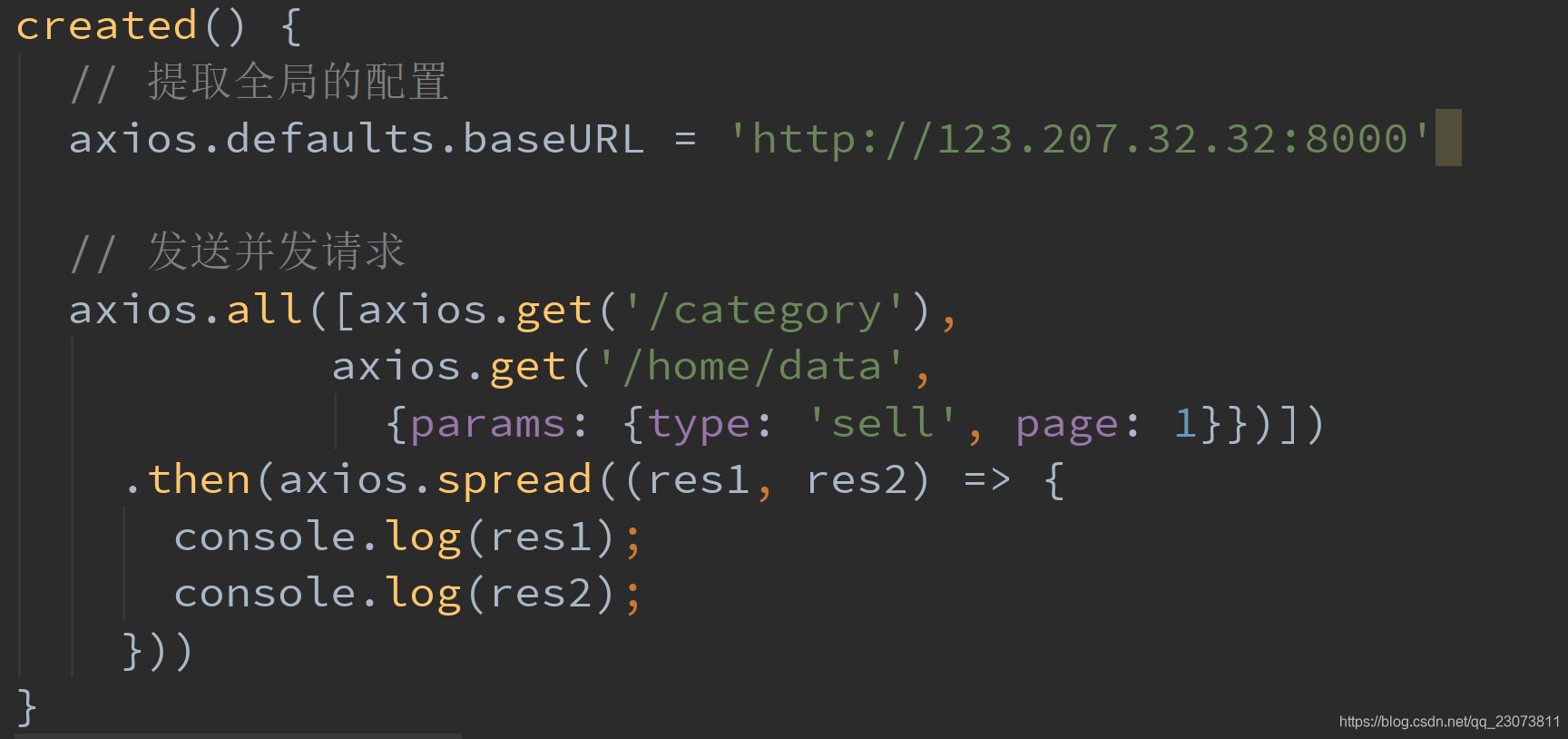
- 代码
// 3.使用全局的axios和对应的配置在进行网络请求
axios.defaults.baseURL = 'http://123.207.32.32:8000'
axios.defaults.timeout = 5000 // 超时
axios.all([axios({
url: '/home/multidata'
}), axios({
url: '/home/data',
params: {
type: 'sell',
page: 5
}
})]).then(axios.spread((res1, res2) => {
// 使用 axios.spread 可将数组 [res1,res2] 展开为 res1, res2
console.log(res1);
console.log(res2);
}))
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
# 4、常见的配置选项
- 请求地址
- url: '/user',
- 请求类型
- method: 'get',
- 请根路径
- baseURL: 'http://www.mt.com/api',
- 请求前的数据处理
- transformRequest:[function(data){}],
- 请求后的数据处理
- transformResponse: [function(data){}],
- 自定义的请求头
- headers:{'x-Requested-With':'XMLHttpRequest'},
- URL查询对象
- params:{ id: 12 },
- 查询对象序列化函数
- paramsSerializer: function(params){ }
- request body
- data: { key: 'aa'},
- 超时设置s
- timeout: 1000,
- 跨域是否带Token
- withCredentials: false,
- 自定义请求处理
- adapter: function(resolve, reject, config){},
- 身份验证信息
- auth: { uname: '', pwd: '12'},
- 响应的数据格式 json / blob /document /arraybuffer / text / stream
- responseType: 'json',
get方法参数放parmas,post方法参数放request body 请求体的data
# 六、axios的实例
# 1、axios的实例
- 为什么要创建axios的实例呢?
- 当我们从axios模块中导入对象时, 使用的实例是默认的实例.
- 当给该实例设置一些默认配置时, 这些配置就被固定下来了.
- 但是后续开发中, 某些配置可能会不太一样.
- 比如某些请求需要使用特定的baseURL或者timeout或者content-Type等.
- 这个时候, 我们就可以创建新的实例, 并且传入属于该实例的配置信息.
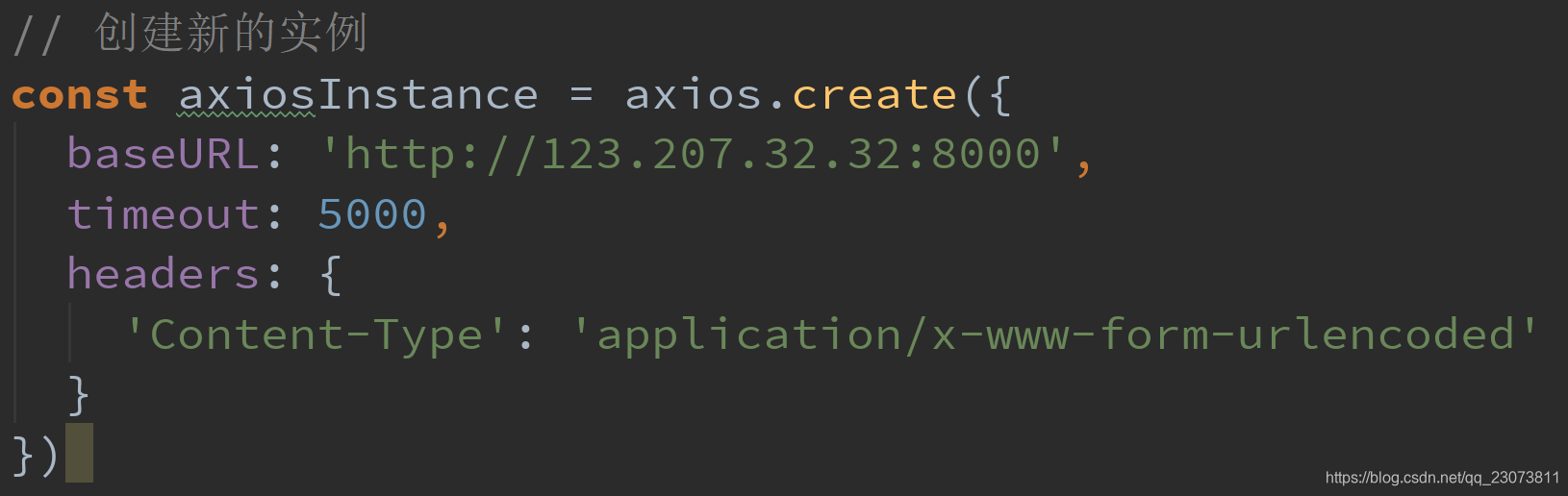

- 代码
// 为什么要创建axios实例?有些请求的配置可能会不同,大项目会有多个服务器,服务器的ip不同,baseURL也就不同
axios.defaults.baseURL = 'http://222.111.33.33:8000'
axios.defaults.timeout = 10000
axios({
url: 'http://123.207.32.32:8000/category'
})
// 4.创建对应的axios的实例
const instance1 = axios.create({
baseURL: 'http://123.207.32.32:8000',
timeout: 5000
})
instance1({
url: '/home/multidata'
}).then(res => {
console.log(res);
})
instance1({
url: '/home/data',
params: {
type: 'pop',
page: 1
}
}).then(res => {
console.log(res);
})
const instance2 = axios.create({
baseURL: 'http://222.111.33.33:8000',
timeout: 10000,
headers: {}
})
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
# 2、axios封装
- 为什么要封装?
- App.vue
<template>
<div id="app">
<div>{{result}}</div>
<h2>-----------------------------------|</h2>
<hello-world/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import HelloWorld from './components/HelloWorld'
import axios from 'axios'
export default {
name: 'App',
components: {
HelloWorld
},
data() {
return {
result: ''
}
},
created() {
axios({
url: 'http://123.207.32.32:8000/home/multidata'
}).then(res => {
// console.log(res);
this.result = res;
})
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
HelloWorld.vue
<template>
<h2>{{categories}}</h2>
</template>
<script>
import axios from 'axios'
// import android from 'android'
export default {
name: "HelloWorld",
data() {
return {
categories: ''
}
},
created() {
axios({
url: 'http://123.207.32.32:8000/category'
}).then(res => {
this.categories = res;
})
// android.ios({
//
// })
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
- 这种开发思路不好,每个组件对第三方框架依赖太强了,假如这个框架不再维护,或者有bug,更换框架得一个个文件查找修改
- 要有这种开发意识:只要引用第三方的东西,千万不要在多个组件对它有依赖
- 那要怎么做?
- 单独建一个文件,对它进行封装
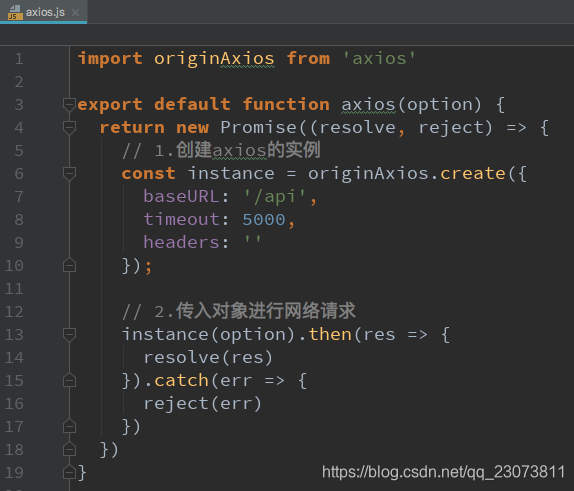
- 新建network文件夹,里面新建文件request.js
- request封装v1.0 使用回调,返回数据
// request.js
import axios from 'axios'
// request封装v1.0 使用回调,返回数据
export function request(config, success, failure) {
// 1.创建axios的实例
const instance = axios.create({
baseURL: 'http://123.207.32.32:8000',
timeout: 5000
})
// 发送真正的网络请求
instance(config)
.then(res => {
// console.log(res);
success(res);
})
.catch(err => {
// console.log(err);
failure(err)
})
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
// main.js
// 5.封装request模块
import {
request
} from "./network/request";
// request封装v1.0 的调用
request({
url: '/home/multidata'
}, res => {
console.log(res);
}, err => {
console.log(err);
})
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
- request封装v2.0 直接传一个 config 再从里面取 success,failure
// request.js
// request封装v2.0 直接传一个config 再从里面取success,failure
export function request(config) {
// 1.创建axios的实例
const instance = axios.create({
baseURL: 'http://123.207.32.32:8000',
timeout: 5000
})
// 发送真正的网络请求
instance(config.baseConfig)
.then(res => {
// console.log(res);
config.success(res);
})
.catch(err => {
// console.log(err);
config.failure(err)
})
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
// main.js
// request封装v2.0 的调用
request({
baseConfig: {
url:'/home/multidata'
},
success: function (res) {
console.log(res);
},
failure: function (err) {
console.log(res);
}
})
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
- request封装v3.0 使用Promise
// request.js
// request封装v3.0 使用Promise
export function request(config) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// 1.创建axios的实例
const instance = axios.create({
baseURL: 'http://123.207.32.32:8000',
timeout: 5000
})
// 发送真正的网络请求
instance(config)
.then(res => {
resolve(res)
})
.catch(err => {
reject(err)
})
})
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
// main.js
request({
url: '/home/multidata'
}).then(res => {
console.log(res);
}).catch(err => {
console.log(err);
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
- request封装v4.0 直接return instance(config) 因为它这个本身就是一个Promise
// request.js
// request封装v4.0 直接return instance(config) 因为它这个本身就是一个Promise
export function request(config) {
// 1.创建axios的实例
const instance = axios.create({
baseURL: 'http://123.207.32.32:8000',
timeout: 5000
})
// 2.发送真正的网络请求
return instance(config) // 本身的返回值就是个promise
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
// main.js
// request封装v3.0 / v4.0的调用
request({
url: '/home/multidata'
}).then(res => {
console.log(res);
}).catch(err => {
// console.log(err);
})
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
# 七、拦截器
# 1、如何使用拦截器?
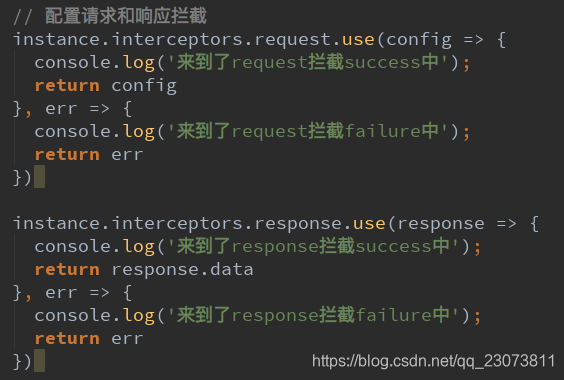
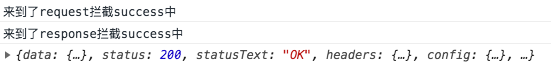
- axios提供了拦截器,用于我们在发送每次请求或者得到相应后,进行对应的处理。
- 如何使用拦截器呢?
- 我们把请求拦截下来后,必须再返回这个请求(即config)
# 2、拦截器中都做什么呢?
# 2.1 请求拦截
- 请求拦截可以做到的事情:
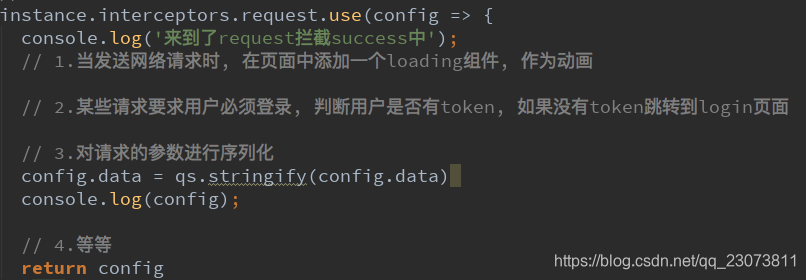
- 请求拦截中错误拦截较少,通常都是配置相关的拦截
- 可能的错误比如请求超时,可以将页面跳转到一个错误页面中。
# 2.2 响应拦截
- 响应拦截中完成的事情:
- 响应的成功拦截中,主要是对数据进行过滤。
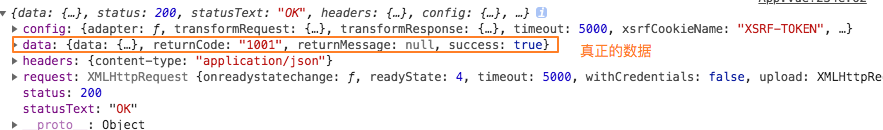

- 响应的失败拦截中,可以根据status判断报错的错误码,跳转到不同的错误提示页面。

// request.js
export function request(config) {
// 1.创建axios的实例
const instance = axios.create({
baseURL: 'http://123.207.32.32:8000',
timeout: 5000
})
// 2.axios的拦截器
// 2.1.请求拦截的作用 成功/失败
instance.interceptors.request.use(config => {
// console.log(config);
// 1.比如config中的一些信息不符合服务器的要求
// 2.比如每次发送网络请求时, 都希望在界面中显示一个请求的图标
// 3.某些网络请求(比如登录(token)), 必须携带一些特殊的信息
// 得把config再返回
return config
}, err => {
// console.log(err);
})
// 2.2.响应拦截 成功/失败
instance.interceptors.response.use(res => {
// console.log(res);
return res.data
}, err => {
console.log(err);
})
// 3.发送真正的网络请求
return instance(config) // 本身的返回值就是个promise
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
// main.js
// request封装v3.0 / v4.0的调用
request({
url: '/home/multidata'
}).then(res => {
console.log(res);
}).catch(err => {
// console.log(err);
})
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
编辑 (opens new window)
上次更新: 2023/09/12, 14:55:44
